
Project Audit Report Template
Being able to identify issues, concerns and challenges within a project before they become problems is a vital skill for any project manager.
The audit report provides an excellent way to identify any problems before they become a risk to the project. It allows the project manger to communicate in a positive manner with his or her sponsor, stakeholders, and each of the project team members by presenting the best way to overcome the concerns, flaws and issues described in the audit report.
The purpose of project audits
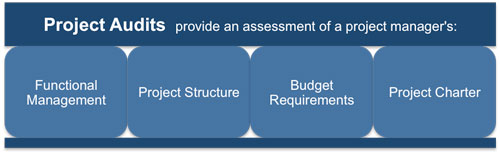
Success within a project relies on recognizing problems with key project areas such as schedule, resource, cost, contract and quality with sufficient time to enable the best way to manage the issue or concern to be identified without compromising the project plan.
The audit report gives the project manager the most up-to-date and relevant data as it is needed so that the exact condition of the project is known at all times and. It also provides feedback to the organization on how well their project management processes and procedures work in practice. It can show areas where training is needed, further guidelines are required and where governance activities must be improved.
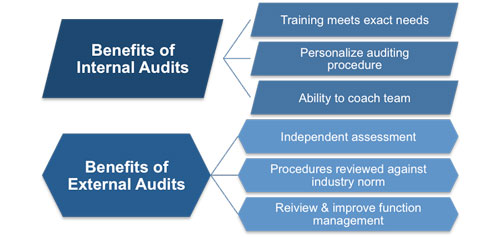
Internal and external audits
Some organizations chose to develop their own auditing skills whilst others find using external auditors is more beneficial to how they operate. The audit report template guides you through what should be included in your report in terms of what:
1) Has been completed in that period
2) Items still outstanding for that period
3) Overview of remaining audit activities
4) Details of Completed Independent Validation
5) Proposed recommendations.
The main purpose of the audit report is to shown how the project is performing at a point in time in accordance to its management plan. For organizations that are subject to high levels of compliance this report performs three quality tasks by assessing the performance of the purchases plus tendering processes, third-party contract management and project procedures.
The roles and responsibilities of those involved in the audit report production need to be described within project management plan and will be shown in the organizational breakdown structure (OBS). This must include a detailed outline of the resources need to perform the number of audits required during its lifespan. The majority of audits follow the basic four-step process shown in the diagram below.
Stages of the project audit
The Post Implementation Review (PIR) is a key project audit and is one that every project manager should insist upon and allow sufficient time and resources to ensure it is performed. It will answer whether or not the project has:
1) Achieved its aim.
2) Been completed in a timely fashion.
3) The final product matches the project scope.
4) Was completed within the project budget.
5) Met customer or end user requirements.
6) Shown to be a sound investment of organizational funds.
7) Used a compatible project methodology.
Project audits provide an ideal opportunity for project managers to assess how well the approach adopted for the project met organizational needs, managed potential risks effectively and allowed sufficient contingency within function management plans.
